Good data governance is essential. As we increasingly rely on digital technologies, effective data governance becomes ever more important. This is especially true for research organizations that manage large volumes…
Good data governance is essential. As we increasingly rely on digital technologies, effective data governance becomes ever more important. This is especially true for research organizations that manage large volumes of data.
Without good governance, data can become inaccurate and siloed. It can be open to security vulnerabilities, which lead to increased risks and financial costs. From mild inefficiencies to regulatory penalties, a lack of data governance can cause a plethora of problems.
Data governance is a part of data management. It ensures good management through the use of policies, processes and standards. It covers the responsibilities and roles that ensure accountability for and ownership of data. Within research funding organizations, there are many benefits to good data governance.
These include better decision-making through consistent data management. They also include efficiencies that enable the re-use of data, reduced costs and better project evaluation. These benefits are crucial for Science Granting Councils (SGCs).
Under the Science Granting Council Initiative (SGCI), a data governance toolkit has been developed. The Centre for Science, Technology, and Innovation Indicators (CeSTII) led its creation. This valuable resource provides guidance that SGCs can use to implement effective data governance.
What is a data governance toolkit?
The Data Governance Toolkit is a practical resource designed to help SGCs strengthen their data governance systems. It draws on the Data Governance Institute’s widely recognized framework. The toolkit adapts the institute’s approach into actionable guidance. It provides step-by-step instructions covering key components of effective data governance. This includes everything from data accountability to data security. The toolkit also includes targeted sections on specific aspects of data governance. Moreover, it includes two dedicated tools to support implementation. The toolkit can help SGCs better implement data governance across their operations. By following its best practices, SGCs can build efficient, robust systems.
What does the data governance toolkit aim to do?
Data governance should be a shared responsibility, and SGC staff can facilitate best practices. With this in mind, the toolkit has several aims. It offers guidelines and tools for assessing and implementing good governance in SGCs.
Sound governance helps to ensure high-quality data. It also supports consistent, reliable data that can be used appropriately within SGCs. It sets responsibilities so that the people working with data know their roles.
The toolkit is aimed at data managers in SGCs. It guides them through the process of implementing a data governance system. The toolkit considers:
- Establishing a data governance structure
- Developing policies and procedures
- Implementing data quality controls
- Managing data privacy and security
- Ensuring compliance with relevant regulations
What does the toolkit contain?
Data governance frameworks create the foundations for good governance. They include, for example, missions and values, beneficiaries, programme outputs, work programmes, processes, and participants.
The data framework is important. It is a function that supports an organizations’ overarching data management strategy.
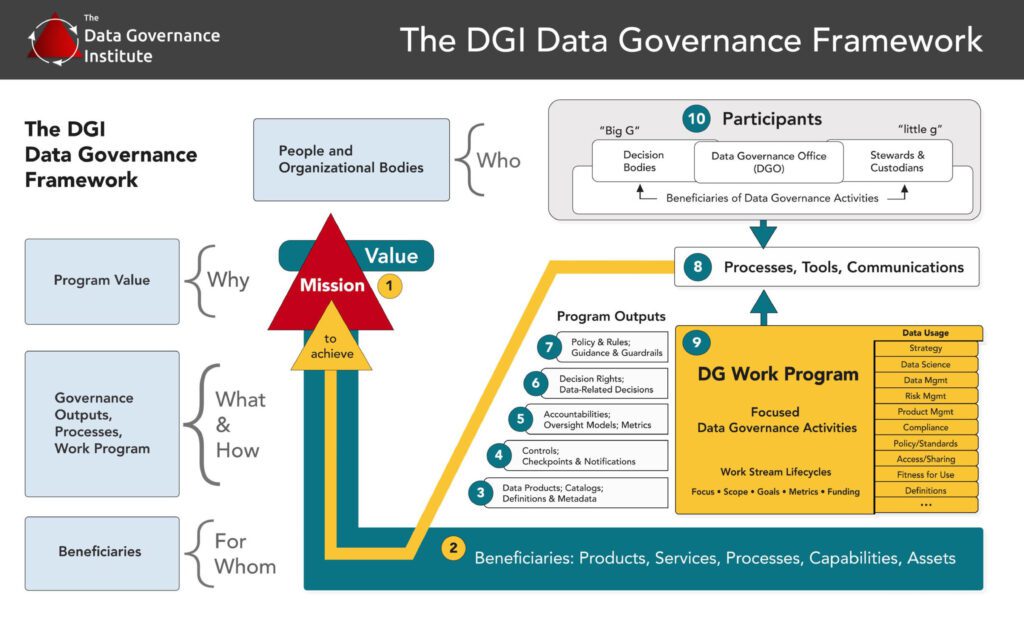
The toolkit also examines the role of data stewards. These are the people in charge of how data is collected, stored, and used. Their actions help good governance succeed. The toolkit examines the different roles of data stewards, from technical to lead, and shows how the roles work together within a data governance office.
Implementing data governance principles is another core section of the toolkit. Here, the toolkit focuses on several subjects. These include:
- Data security
- Data storage and accessibility
- Data quality, integrity and reliability
These areas of governance are critical to the smooth running of data management. They ensure that data is available when needed, protect data from cyber-attacks and system failures, and ensure that the data can be trusted. This is important for turning information into a strategic decision-making asset for SGCs.
Two tools: Maturity Assessment and RAC
The toolkit also includes two useful tools. SGCs can use the maturity assessment tool to measure progress in their data governance journey. This tool identifies five levels of governance maturity in an SGC: initial, reactive, managed, proactive, and transformational.
Understanding where an SGC is about its data governance journey helps to define what the next steps are needed.

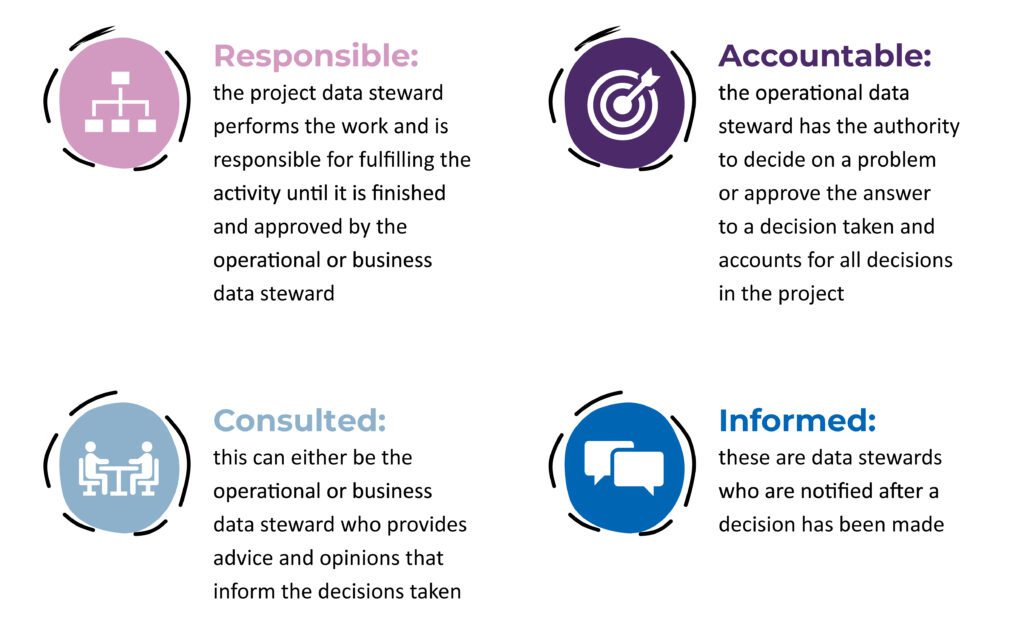
SGCs can use the RACI tool to assess and manage roles and responsibilities for data stewards. RACI stands for Responsible, Accountable, Consulted and Informed.
It is a method for identifying, assigning and tracking roles and responsibilities for specific data activities, projects and tasks. This is important for avoiding duplication of effort and improving data management accountability.
– Practical steps for implementing a data governance strategy.
The toolkit identifies several practical steps for implementing a data governance strategy. Before creating a data governance programme, construct a data governance mechanism. This begins with policy development to define governance goals and strategies. Then establish data governance structures for the organisation. Finally, establish data governance procedures to enhance the process.
– How should the toolkit be used?
Work your way step by step through the toolkit. The various sections cover how to create a data governance structure, develop policies and practices etc. The data governance maturity assessment tool also helps users evaluate the effectiveness of their data governance system. Moreover, it identifies areas for improvement. Adapt the tools to the specific needs and priorities of individual SGCs and use the Excel file and template to help.
Learn more about the Data Governance Toolkit
Finally, The toolkit includes a case study on data governance at CeSTII. Specifically, it focuses on how CeSTII governs survey data usage for South Africa’s Department of Science and Innovation. CeSTII is not responsible for grants management.
However, it collects and manages STI survey data that is made publicly available. The case study reveals the step-by-step process that CeSTII has implemented for data access.
The data governance toolkit is a valuable resource for SGC data managers. It provides concrete advice and best practices for creating and developing robust governance structure.
Themes
The SGCI aims to strengthen the capacities of these SGCs to support research and evidence-based policies that will contribute to economic and social development.

